Larval Development of Helminths Occurs in Which Host
Figure 1 Helminth-induced pathogenesis of human pulmonary disease. Mating occurs in this host.

Human Soil Transmitted Helminths And Lung Infections A Guide Review For Respiratory Therapists Atlantis Press
For eggs in moist soil at optimal temperature and oxygen levels the embryo develops into an infective larva after 2 to 4 weeks named second-stage larva.
. Primary host intermediate secondary host definitive host transport host Mating takes place in all hosts. When a eukaryotic cell is not undergoing mitosis the DNA and its associated proteins appear as a visible network of dark fibers called the. The coracidium develops into a procercoid stage in its micro-crustacean first immediate host and then into a plerocercoid larva in its next intermediate host which is a vertebrate.
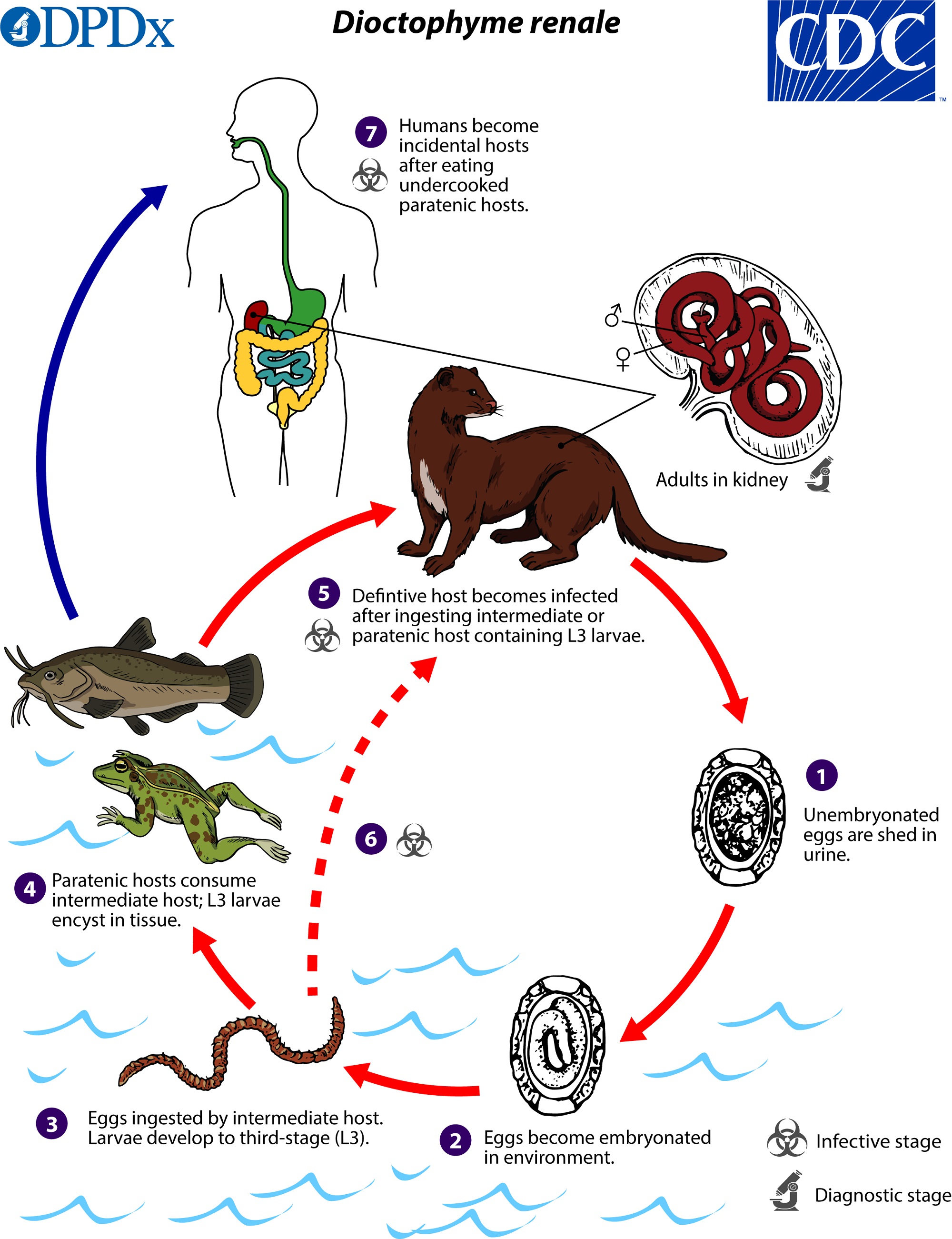
In some cases the intermediate vector transmits infective stages when it bites the host to take a blood meal the arthropod vectors of filarial worms. Spread to humans by Consumption of meat containing larvae. Larval development of helminths occurs in which host.
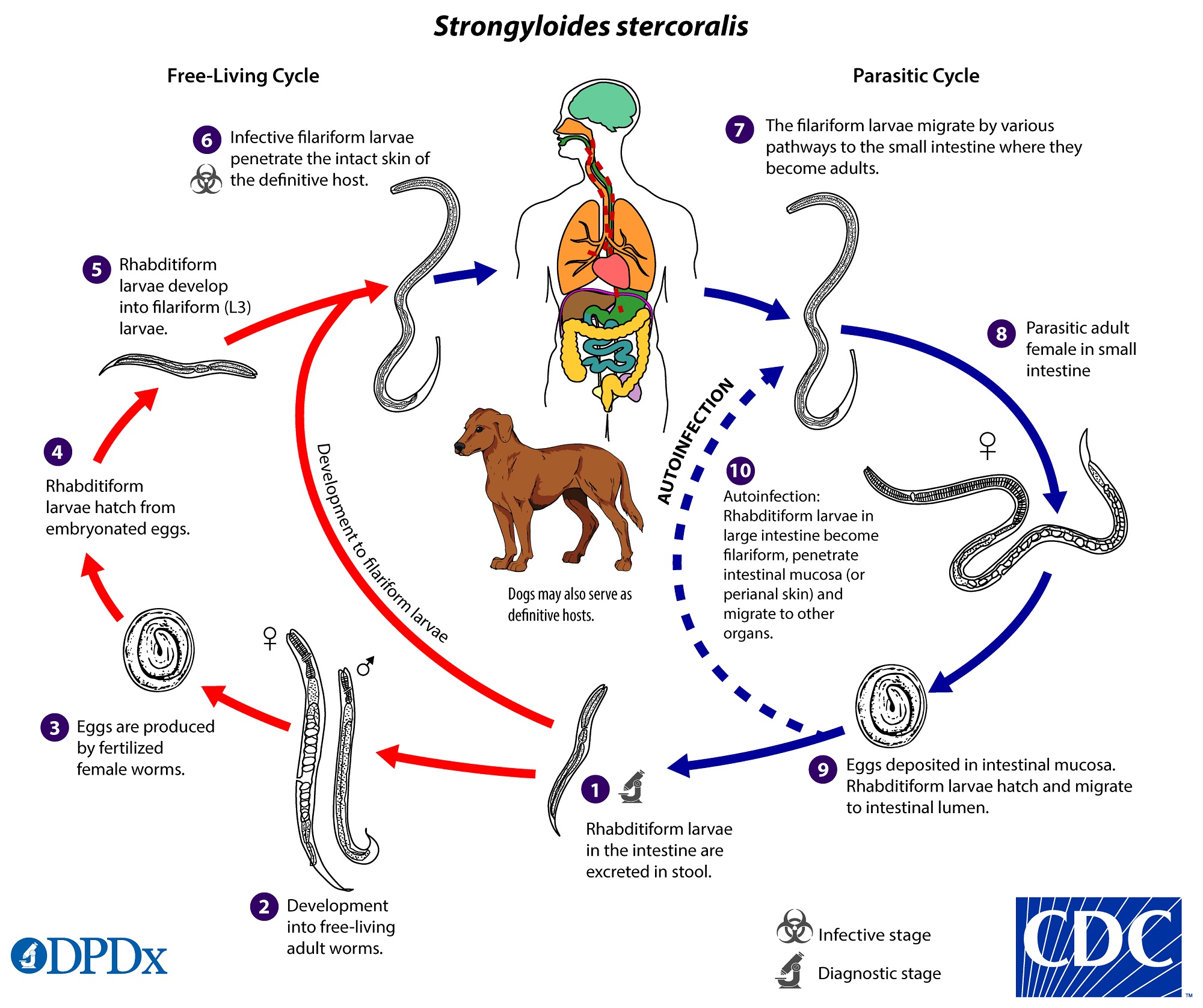
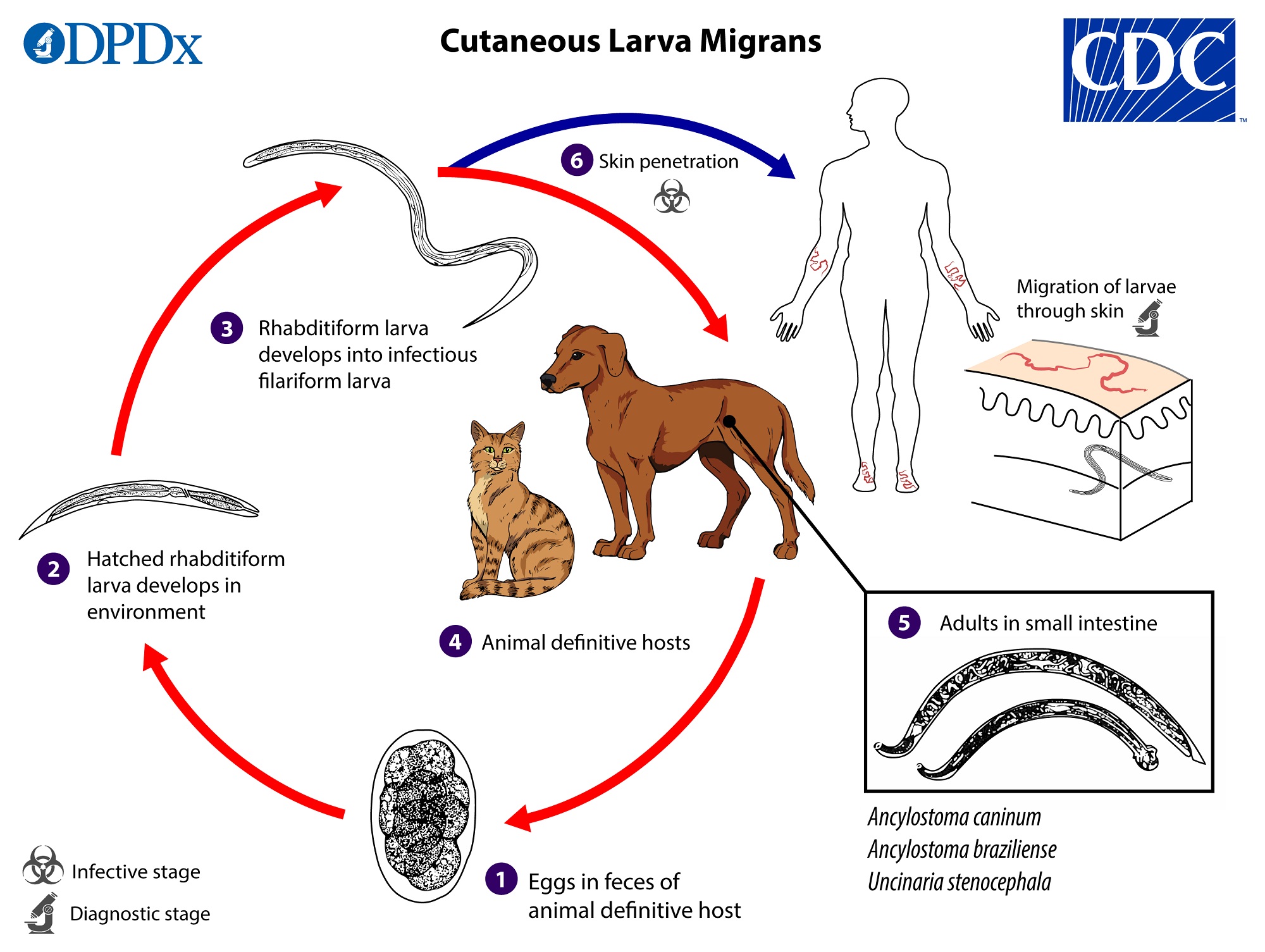
The simplest is by accidental ingestion of infective eggs Ascaris Echinococcus Enterobius Trichuris or larvae some hookworms. The egg enters an intermediate host. Larvae and eggs are developmental forms of.
The helminth develops into an adult in this host. Major Parasitic Helminths Roundworms Intestinal Nematodes Infected in larval stage. Known as athletes foot Cilia are structures for motility found primarily in.
Common name of disease or worm Trichina worm. Larval development of helminths occurs in which host. Intermediate host Eukaryotic flagella differ from prokaryotic flagella because only eukaryotic flagella Contain microtubules.
Multiple Choice intermediate transport transport definitive intermediate definitive transport intermediate definitive transport. In humans Helminths generally infect the. Mating occurs in all hosts.
Are identified in the laboratory by microscopic examination of body fluids and excretions containing the eggs and larvae. The plerocercoid larva develops into an adult worm in the definitive final host. In eukaryotic cells ribosomes have two locations.
Fertilized eggs are released into the environment where they can infect another host. The ____ is a cellular form of some protozoans which can resist survive harsh environmental conditions. Helminth infections can cause pulmonary pathology due to larval migration through the lung vasculature or through the lung tissue causing a diffuse lung disease.
Mating of the adult occurs in the definitive host. Larval development occurs in the host. Larval development of helminths occurs in which host.
The egg releases larvae. Asked Apr 11 2021 in. Larval development of helminths occurs in which host.
Mating takes place in all hosts. Larvae hatch from eggs either inside or outside the host depending on the type of helminth. In several cases infection requires an intermediate host vector.
Larvae develop into an adult in the definitive host. Scattered in the _____ and on the surface of _____. Host requirement Pigs wild mammals.
Additionally trapped larvae or eggs can cause focal lesions within the lungs. Asked Aug 7 2019 in. In other cases the larvae are contained in the tissues of the intermediate host and are taken in when a human eats that host Clonorchis in fish tapeworms in meat and fish Trichinella in meat.
Adulthood and mating of helminths occur in which host. Activities of fungi that are considered detrimental from a human perspective. Helminths are transmitted to humans in many different ways.
Assessment Saved Help During the life cycle of a parasitic helminth development of larvae occurs in the host while mating between adults occurs into 6 host. Larval development of Helminths occurs in which host. Larval development of helminths occurs in which host.
Intermediate secondary host C. Larval development occurs in this host. Other worms have larvae that actively penetrate the skin hookworms schistosomes Strongyloides.

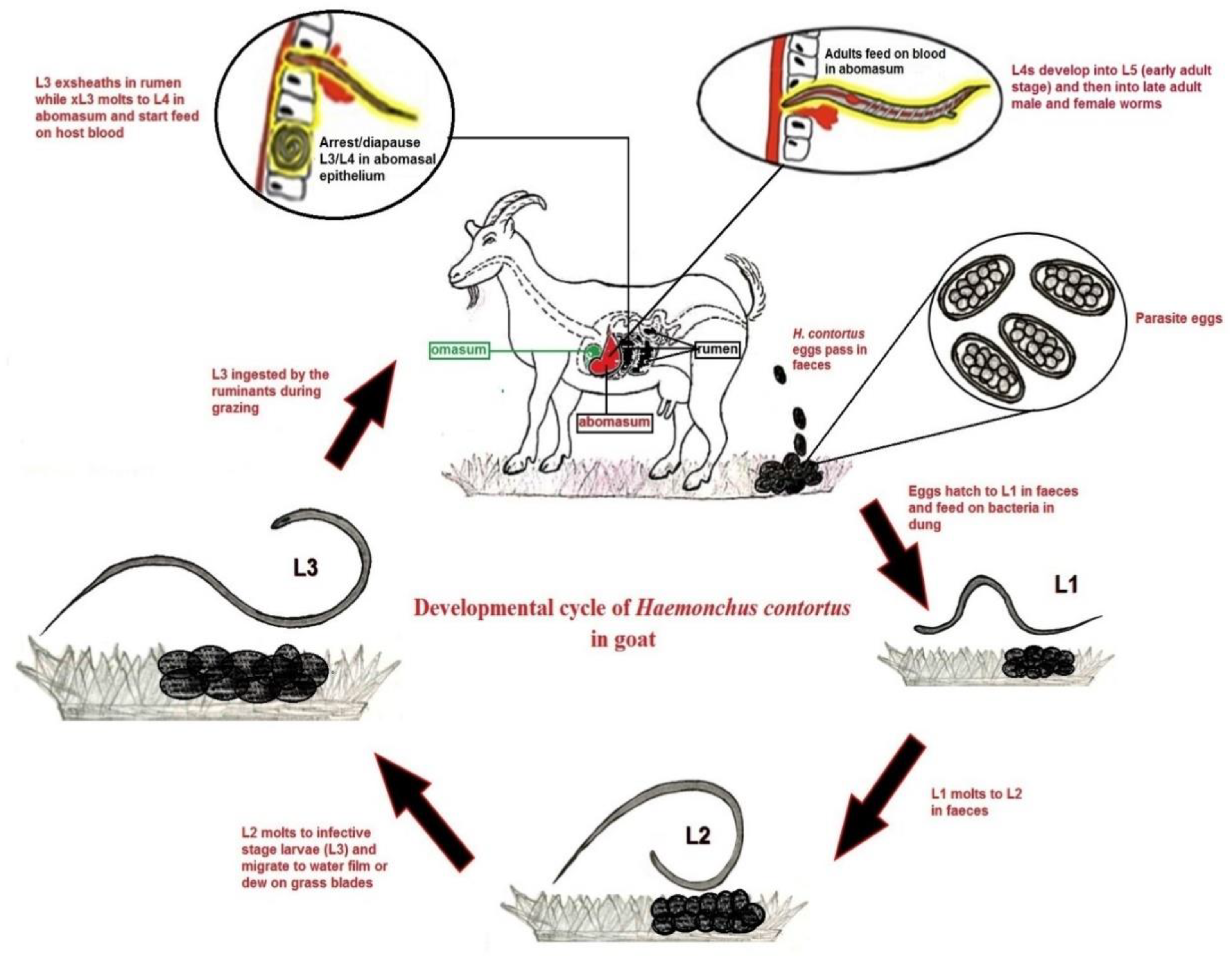
Vaccines Free Full Text Advances In The Development Of Anti Haemonchus Contortus Vaccines Challenges Opportunities And Perspectives Html

Macroparasite An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
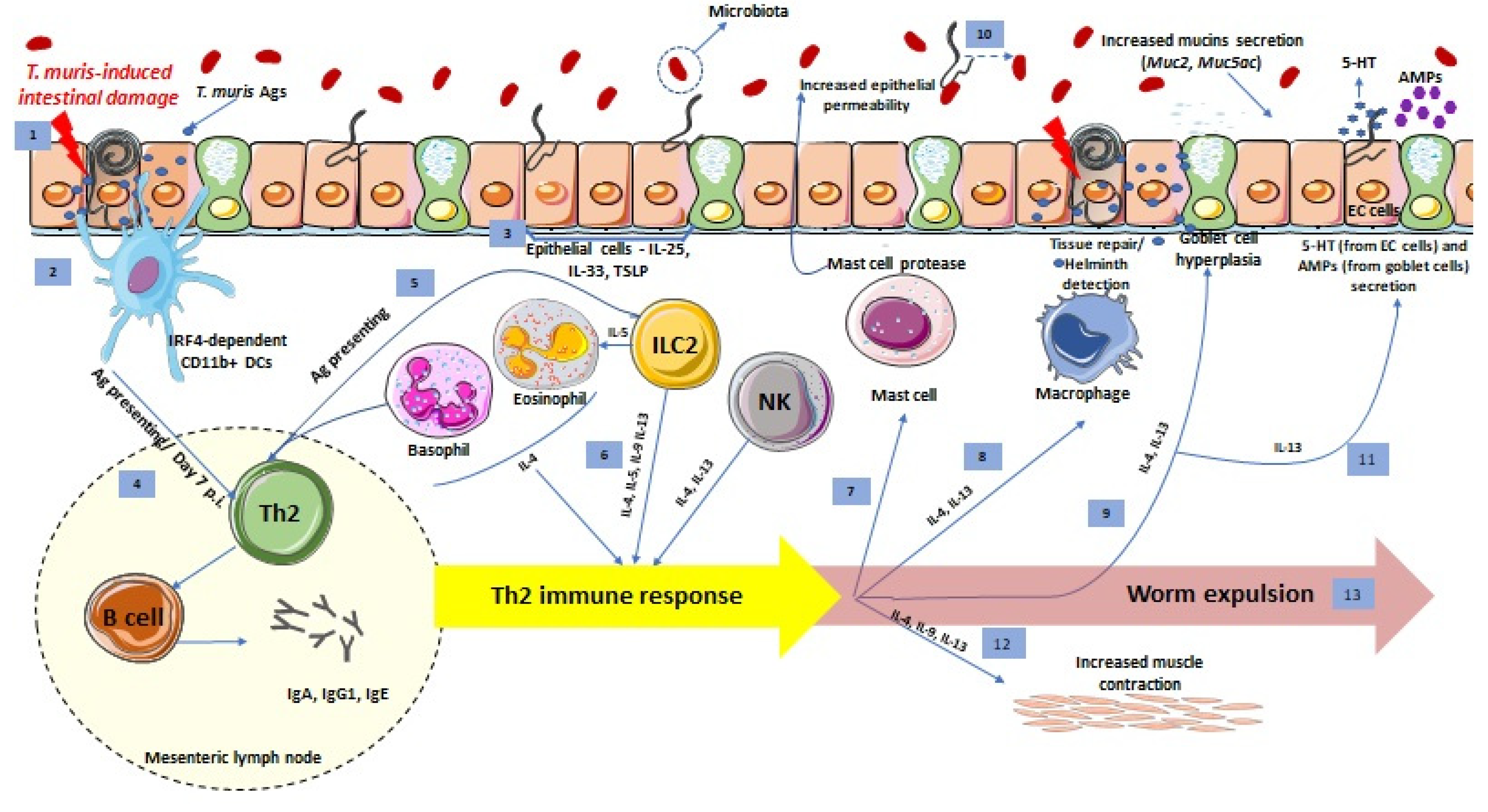
Pathogens Free Full Text Trichuris Muris Model Role In Understanding Intestinal Immune Response Inflammation And Host Defense Html
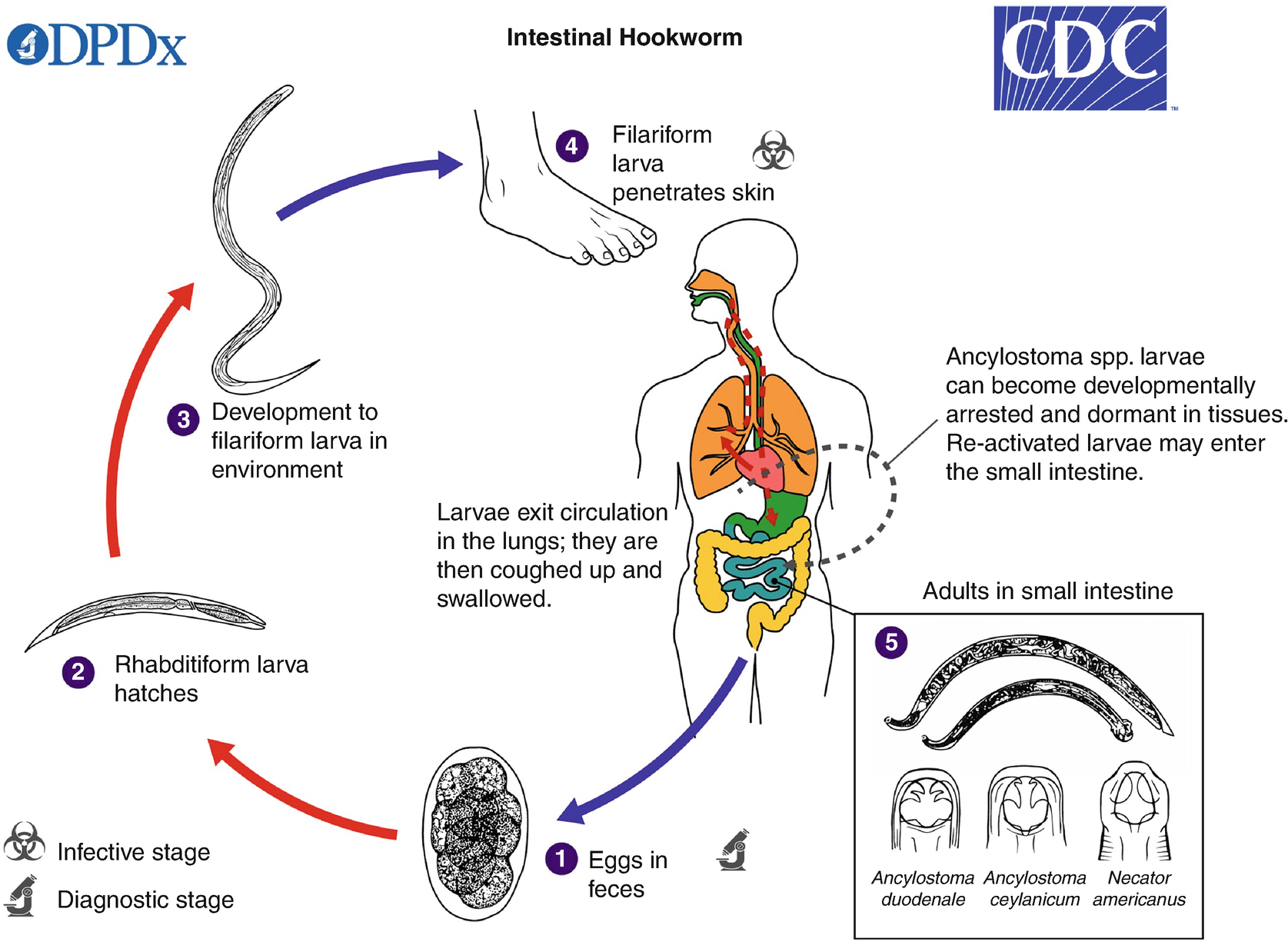
Human Helminth Infections A Primer Springerlink

Ancylostoma Duodenale And Necator Americanus Lifecycle Parasite Life Cycles Intestinal Parasites

Hookworm Infection Toward Development Of Safe And Effective Peptide Vaccines Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology

Bentonite Parasite Cleanse Parasite Intestinal Parasites Skin Ulcer

Optimal Growth Strategies Of Larval Helminths In Their Intermediate Hosts Parker 2003 Journal Of Evolutionary Biology Wiley Online Library
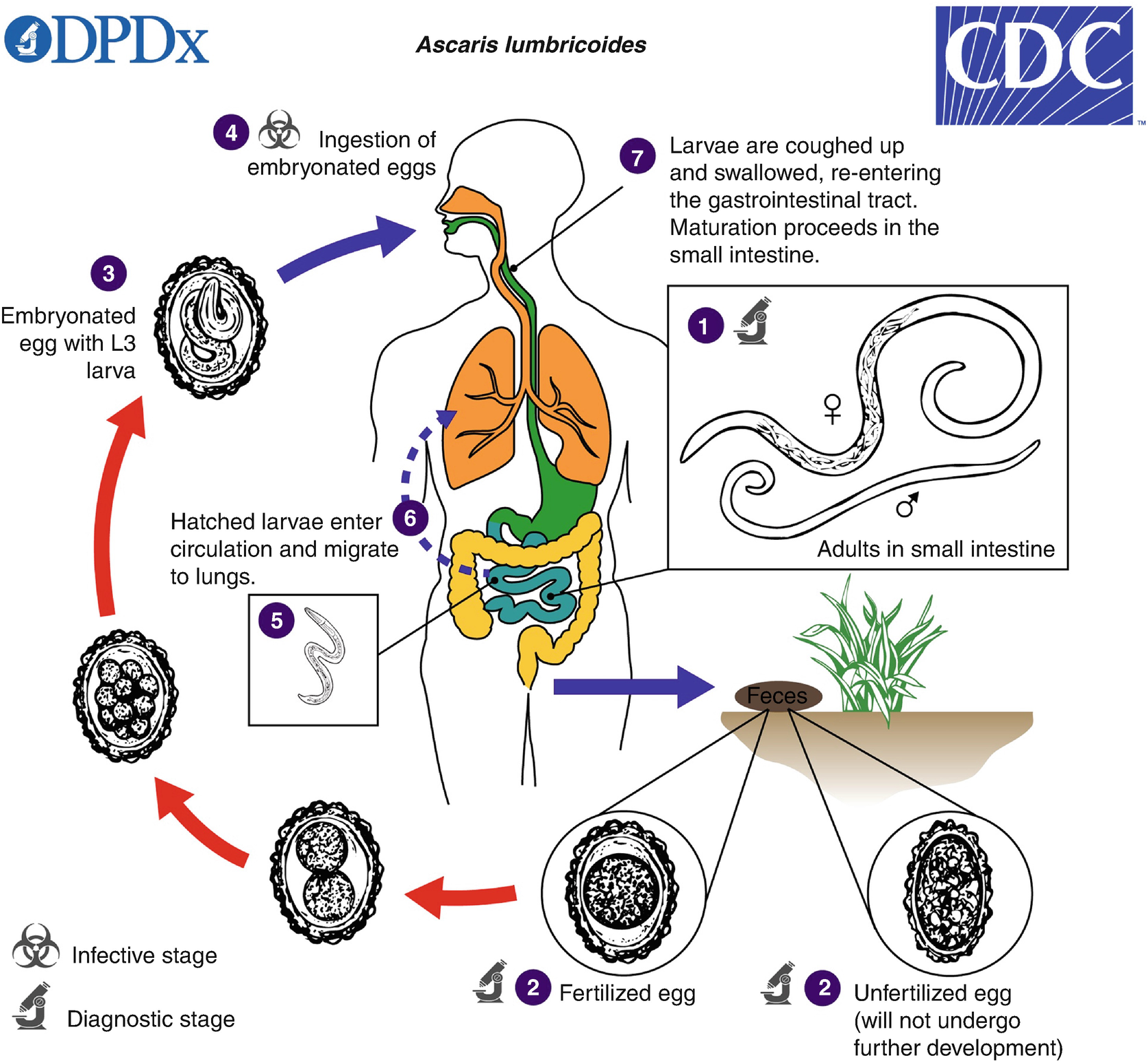
Human Helminth Infections A Primer Springerlink

Trichinella Spiralis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

The Chinese Liver Fluke Clonorchis Sinensis Is A Species Of Parasitic Worm That Is Classified Within The Digenea Ph Liver Fluke Parasitic Worms Invertebrates

Helminth Eggs And Larva The Protozoan Blood Parasite Found Scale Download Scientific Diagram

Hatching Of Parasitic Nematode Eggs A Crucial Step Determining Infection Trends In Parasitology

Typical Furcocercous Type Forked Tail Cercaria Of The Family Schistosomatidae The Cercaria Of Schistosome Rectangle Glass Contaminated Water Better Living

Hatching Of Parasitic Nematode Eggs A Crucial Step Determining Infection Trends In Parasitology

Advances In Vaccine Development For Human Lymphatic Filariasis Trends In Parasitology
Comments
Post a Comment